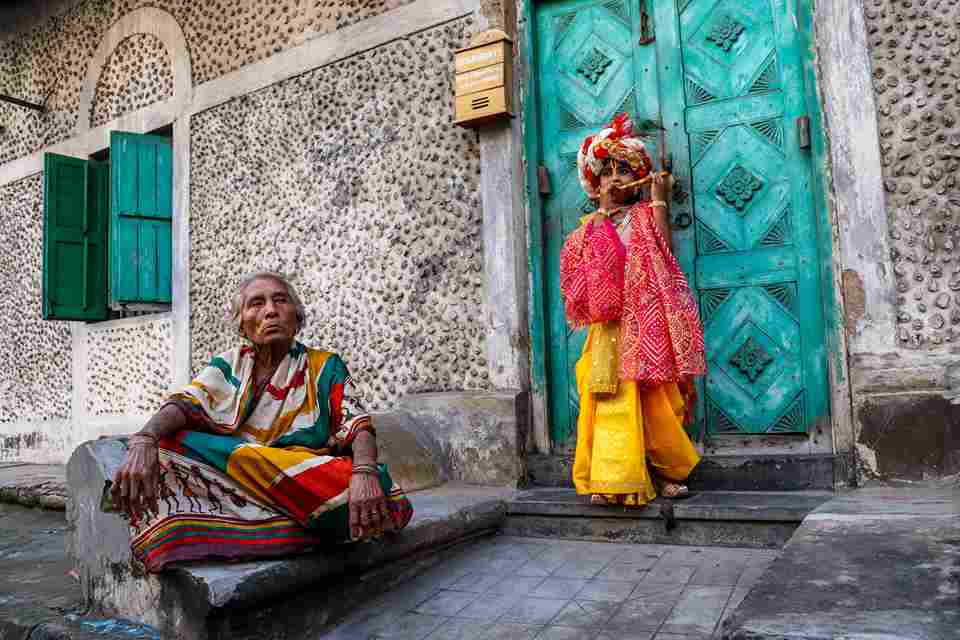India, often called the “Land of Diversity,” is renowned for its rich cultural heritage, linguistic variety, and millennia-old traditions. With a history spanning thousands of years and a population exceeding 1.3 billion, India is a mosaic of cultures, religions, languages, and traditions coexisting harmoniously. This essay explores India’s diversity, examining its cultural, linguistic, religious, and geographical facets, along with the challenges and benefits it offers.
Cultural Diversity
1. Historical Perspective
India’s cultural diversity can be traced back to its ancient history, dating back to the Indus Valley Civilization, which existed around 2500 BCE. This civilization was marked by advanced urban planning, complex social structures, and diverse cultural influences. Over time, various dynasties, such as the Mauryas, Guptas, Mughals, and British, left indelible imprints on Indian culture, resulting in a rich amalgamation of customs, rituals, and art forms.
2. Festivals and Traditions
One of the most vivid expressions of India’s cultural diversity is its plethora of festivals and traditions. From Diwali, the Festival of Lights, celebrated by Hindus, to Eid al-Fitr, observed by Muslims, and Christmas, celebrated by Christians, India celebrates a myriad of festivals with great fervor and enthusiasm. Each region has its own unique customs and rituals, making every festival a grand spectacle.
3. Arts and Crafts
India’s artistic diversity is also reflected in its myriad art forms and crafts. The intricate designs of Madhubani paintings, the vibrant colors of Rajasthani miniature art, and the rhythmic movements of Bharatanatyam and Kathakali dance forms are just a few examples of India’s artistic richness.
4. Cuisine
Indian cuisine is celebrated worldwide for its diversity and flavor. From the spicy dishes of the South to the aromatic biryanis of the North, and from the vegetarian delights of Gujarat to the seafood feasts of coastal regions, India offers a wide array of culinary experiences. The use of spices, herbs, and regional ingredients makes Indian cuisine a journey of taste and culture.
II. Linguistic Diversity
1. A Tower of Babel
India boasts an astounding linguistic diversity, with more than 19,500 languages and dialects spoken across the country. While Hindi and English are the official languages, India recognizes 22 officially recognized languages, each with its own script and unique linguistic characteristics. The Constitution of India recognizes this linguistic diversity and safeguards the rights of linguistic marginalized groups.
2. Regional Languages
The linguistic diversity in India is particularly evident at the regional level. States like Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, West Bengal, and Maharashtra have their own languages, Tamil, Kannada, Bengali, and Marathi, respectively, alongside Hindi or English. These regional languages are the lifeblood of local culture and identity.
3. Preserving Indigenous Languages
Despite the vast number of languages in India, several indigenous languages are facing the threat of extinction due to globalization and urbanization. However, concerted efforts are being made by the government and non-governmental organizations to document, preserve, and promote these endangered languages to ensure that India’s linguistic diversity continues to thrive.
III. Religious Diversity
1. A Multireligious Nation
India is the birthplace of several major religions, including Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. It is also home to significant populations of Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, Buddhists, Jains, and people of other faiths. The coexistence of multiple religions has led to a diverse religious landscape where places of worship for various faiths stand side by side.
2. Religious Tolerance
Religious tolerance is a cornerstone of Indian society. The Constitution of India guarantees freedom of religion to all its citizens, allowing them to practice their faith without discrimination. This commitment to religious freedom has allowed people of different religions to live harmoniously, celebrating each other’s festivals and traditions.
3. Religious Festivals
Religious festivals in India are grand affairs that bring communities together, transcending religious boundaries. Diwali, Eid, Christmas, Holi, and Guru Nanak Jayanti are celebrated with enthusiasm by people of all faiths. This intermingling of religious celebrations fosters unity and mutual respect among diverse religious communities.
IV. Geographical Diversity
1. Varied Landscapes
India’s geography is astounding, encompassing the snow-covered Himalayan peaks in the north, lush tropical forests of the Western Ghats in the south, the arid Thar Desert in the west, fertile Ganges and Brahmaputra plains in the north, and coastal regions along the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal, contributing to its geographic diversity.
2. Climate Zones
India experiences a wide range of climatic conditions, from the arid deserts of Rajasthan to the humid subtropical climate of the Gangetic plains and the tropical climate of the southern states. This diversity in climate has a significant impact on agriculture, biodiversity, and the way of life in different regions.
3. Biodiversity
India’s diverse geography has given rise to a rich biodiversity. The country is home to numerous species of flora and fauna, including the Bengal tiger, Indian elephant, Asiatic lion, and a wide variety of birds and plants. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect this biodiversity and maintain ecological balance.
Benefits of Diversity in India
- Cultural Enrichment: India’s cultural diversity has led to a vibrant and dynamic society, where people from different backgrounds contribute to a rich tapestry of art, music, literature, and traditions.
- Economic Opportunities: The diverse culture and languages of India have opened up a vast market for businesses and industries. Companies can tap into diverse consumer preferences and markets.
- Learning Opportunities: The coexistence of multiple languages and cultures provides individuals with unique learning experiences and helps foster tolerance and understanding.
- Tourism: India’s diverse landscapes, cultural heritage, and festivals attract tourists from around the world, contributing significantly to the economy.
Challenges of Diversity in India
- Linguistic Barriers: The vast linguistic diversity can sometimes create communication barriers, hindering effective governance and education.
- Communal Tensions: Despite the overall harmony, India has experienced communal tensions and conflicts at various points in its history, highlighting the need for continued efforts to promote religious tolerance.
- Regional Disparities: Geographical diversity can also lead to regional disparities in development, access to resources, and opportunities, which the government must address.
- Preservation of Culture: Ensuring the preservation of indigenous languages and cultures is an ongoing challenge, as globalization can erode local traditions.
Conclusion
India’s diversity is its greatest strength, making it a nation like no other. India’s diversity shapes its identity and character in the modern world. While challenges do exist, the benefits of this diversity far outweigh them. India must safeguard its diversity, as it defines its uniqueness.